Introduction
In recent months, a new variant of the mpox virus has raised concerns among public health professionals. Originating in Africa, this variant is believed to cause more severe illness compared to previous strains. As it continues to spread, its potential impact on the United States is being closely monitored by experts and institutions, especially the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Understanding Mpox
The mpox virus, caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), has been known to science since it was first identified in monkeys in Denmark back in 1958. The first human case was later reported in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970. Despite its long history, its global impact remained relatively contained until the outbreak between 2022 and 2023. Symptoms of mpox include a painful rash, enlarged lymph nodes, and fever. It primarily spreads through direct human-to-human contact, including touching, kissing, and sexual activities, as well as contact with contaminated materials or animals.
Recent Developments
The recent variant spreading across Africa is particularly concerning because it appears to cause more severe symptoms. This has prompted a response from public health authorities worldwide to prevent a potential global health crisis. Experts in infectious diseases, while cautiously optimistic, are not taking any chances and are urging for proactive measures to mitigate the risk.
Transmission and Symptoms
Mpox spreads mainly through close physical contact. This includes touching an infected person's lesions, kissing, or engaging in sexual activities. Additionally, the virus can be transmitted through contact with contaminated materials like bedding or clothing and from animals to humans. Infected individuals typically exhibit symptoms such as a painful rash, swollen lymph nodes, and fever, making early detection and isolation crucial in preventing its spread.
Vaccination Efforts
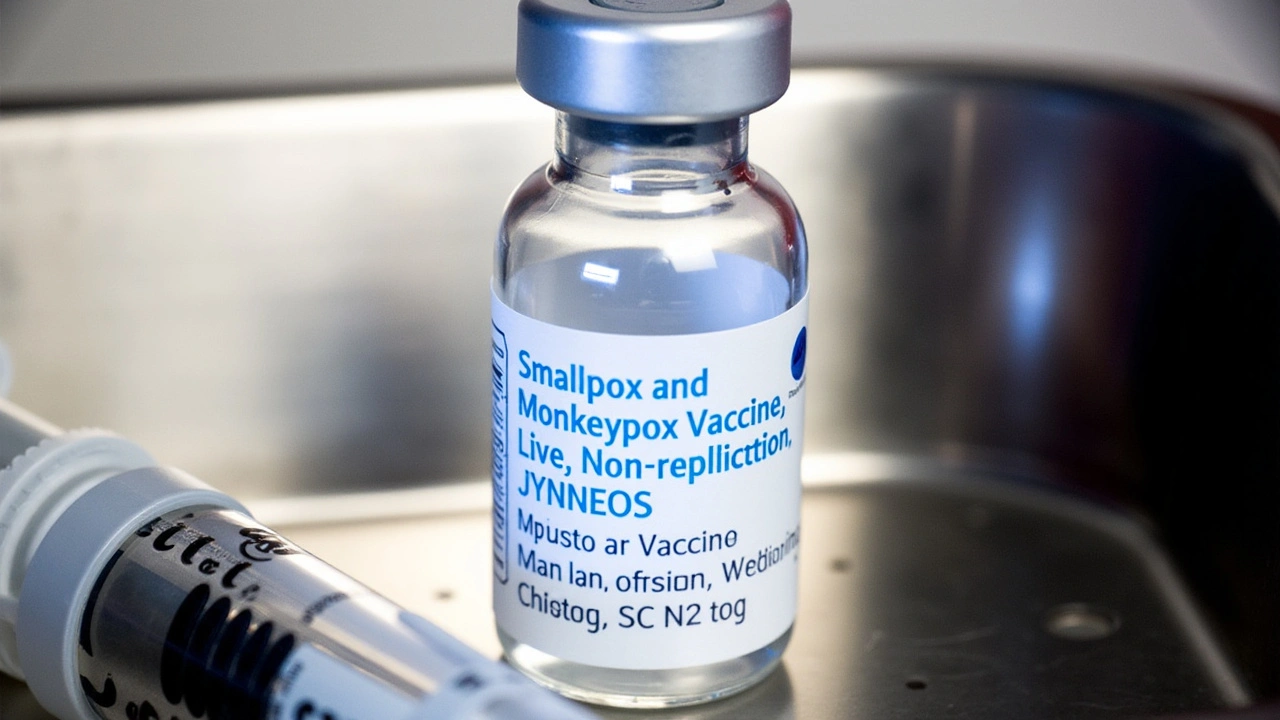
The global outbreak in 2022-2023 underscored the necessity for vaccination, especially among high-risk groups. Among these are frontline health workers, men who have sex with men, and people with multiple sexual partners. The JYNNEOS vaccine, initially developed for smallpox, has been recommended for use against mpox as well. This vaccination effort is a critical component of the global strategy to contain the virus and prevent severe cases.
CDC's Role and Guidelines
The CDC has been at the forefront in monitoring the unfolding situation. They have provided detailed guidelines for clinicians, laboratories, and health departments aimed at identifying and managing mpox cases. These guidelines emphasize the importance of vaccination, supportive care, and stringent infection control measures. The CDC's proactive stance is vital in ensuring that health professionals are prepared to tackle any potential outbreak.
Global Public Health Implications
Despite the best efforts to contain the outbreak, there's an underlying fear that the virus could spread globally, leading to a public health emergency. Experts are calling for a coordinated public health response to handle the situation effectively. This involves international cooperation, timely exchange of information, and harmonized public health measures. Vigilance and adherence to health guidelines are essential to prevent the new mpox variant from causing significant harm in the U.S. and beyond.

Conclusion
As the world watches the progression of the new mpox variant, it's imperative that both the public and health authorities remain vigilant. The threat it poses is undeniable, but through coordinated efforts, vaccination, and adherence to health guidelines, its impact can be mitigated. The importance of a proactive approach cannot be overstated, as it is the best defense against a potential health crisis.





Lemuel Belleza
August 19, 2024 AT 01:19This sounds like another overblown health scare.
faye ambit
September 11, 2024 AT 04:52The rise of a more virulent mpox variant undeniably calls for heightened public awareness. It is essential to recognize that viruses evolve and our collective response must evolve alongside them. Vaccination campaigns, especially targeting high‑risk groups, remain a cornerstone of containment. Equally important is the dissemination of clear, evidence‑based guidelines that respect individual autonomy while protecting community health. Transparent communication can bridge gaps between scientific authorities and the general public. Moreover, fostering empathy towards those affected reduces stigma and encourages timely medical attention. The CDC’s proactive stance, including updated diagnostic protocols, reflects a solid public‑health strategy. Collaboration across borders enables rapid data sharing, which is vital for tracking the variant’s spread. Ultimately, a balanced approach that combines scientific rigor with compassionate outreach offers the best defense against escalation.
Subhash Choudhary
September 22, 2024 AT 18:39Honestly, I’ve been following the news just to stay safe and not panic. The details about the new strain are pretty clear-they say it’s harsher, but the transmission routes haven’t changed. If you avoid close contact with lesions and practice good hygiene, you’re already reducing risk a lot. I think the CDC’s updated guidelines are solid, especially the emphasis on vaccination for frontline workers. For most of us, staying informed and getting the JYNNEOS shot if eligible is the smartest move. It’s not worth overreacting, but ignoring the warnings would be careless.
Ethan Smith
October 15, 2024 AT 22:12The CDC’s recommendation to use the JYNNEOS vaccine aligns with the best available evidence. Clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in preventing severe mpox outcomes, particularly among immunocompromised individuals. Additionally, the guidance to isolate confirmed cases for at least 21 days minimizes community transmission. Health providers are also urged to report suspect cases promptly to facilitate contact tracing. By adhering to these protocols, we can collectively dampen the potential impact of the new variant.
Evelyn Monroig
November 8, 2024 AT 00:45Don’t be fooled by the CDC’s polished press releases; they’re hiding the true scope of the threat. The vaccine they push is just a tool to control the population under the guise of public health. Independent labs have already flagged mutations that could bypass current immunizations. Wake up and question the narrative before it’s too late.
Gerald Hornsby
December 1, 2024 AT 04:19The world teeters on the edge of a silent storm. Each new case is a whisper of impending chaos. Vaccines rise like shields in a battlefield of unseen foes. Knowledge becomes the lantern in a tunnel of darkness. Fear fuels complacency, and complacency feeds disaster. We must act now, or history will write us out. Unity is our only armor against the spread. Preparation is not paranoia; it is prudence. The virus does not care for borders, but we can draw them with vigilance. Every infected soul is a cautionary tale. Science offers us a map, but we must choose the path. Ignorance is a luxury we can no longer afford. Humanity has faced plagues before; we will not falter this time. Stay informed, stay safe, stay resilient :)